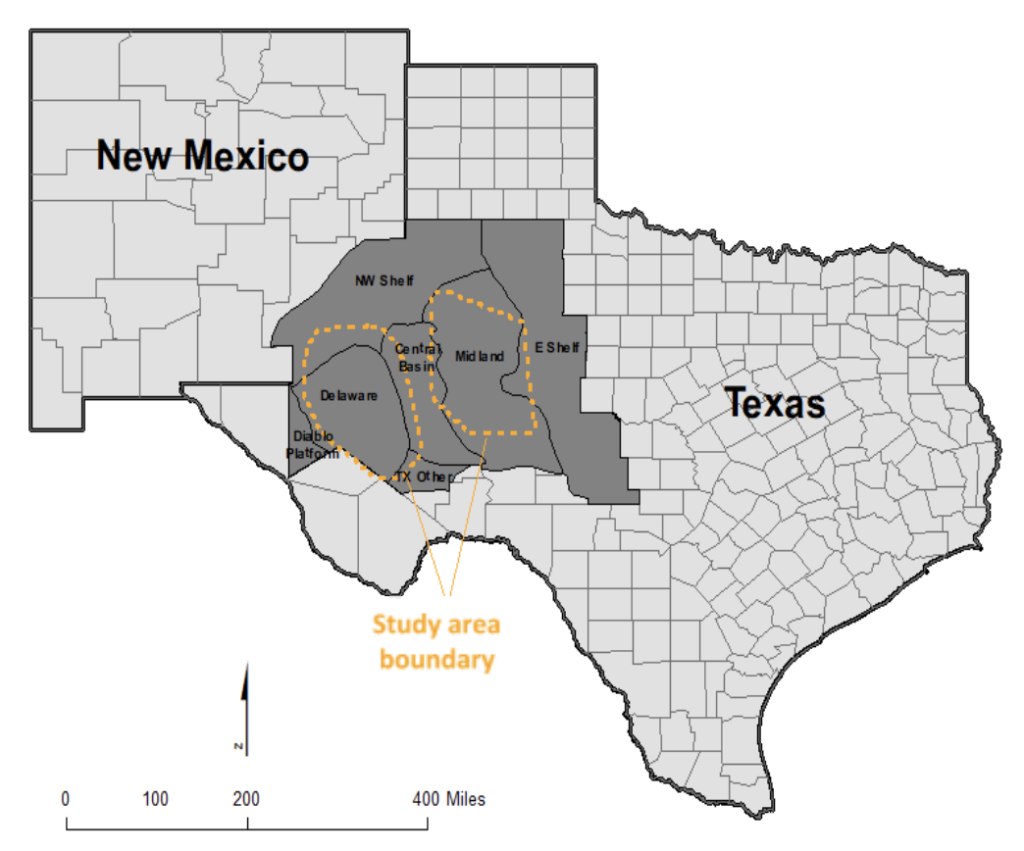
Study Area and Model Parameters
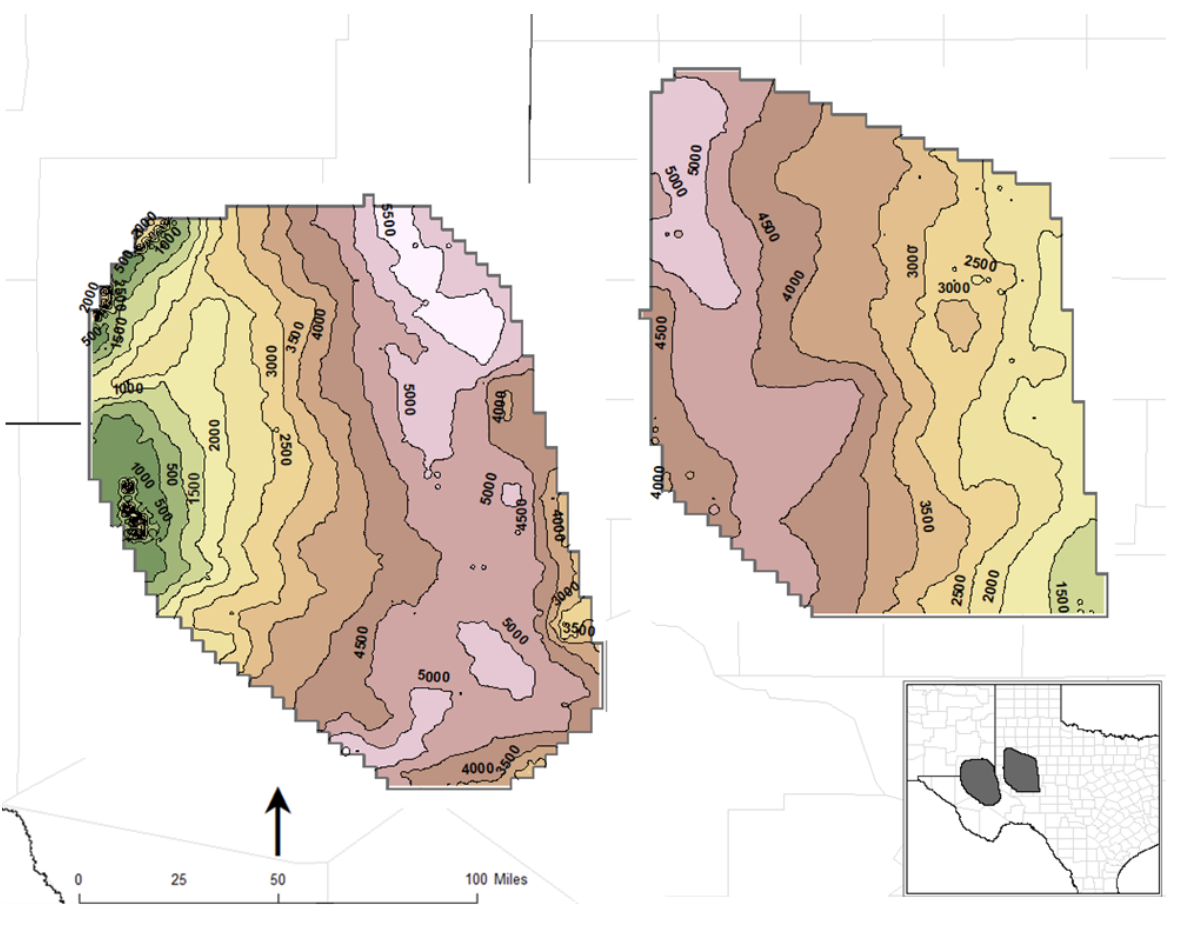 Figure 2. Depth to top of formation for the DMG and SA. Contours in feet from mean sea level. Source: Enverus.
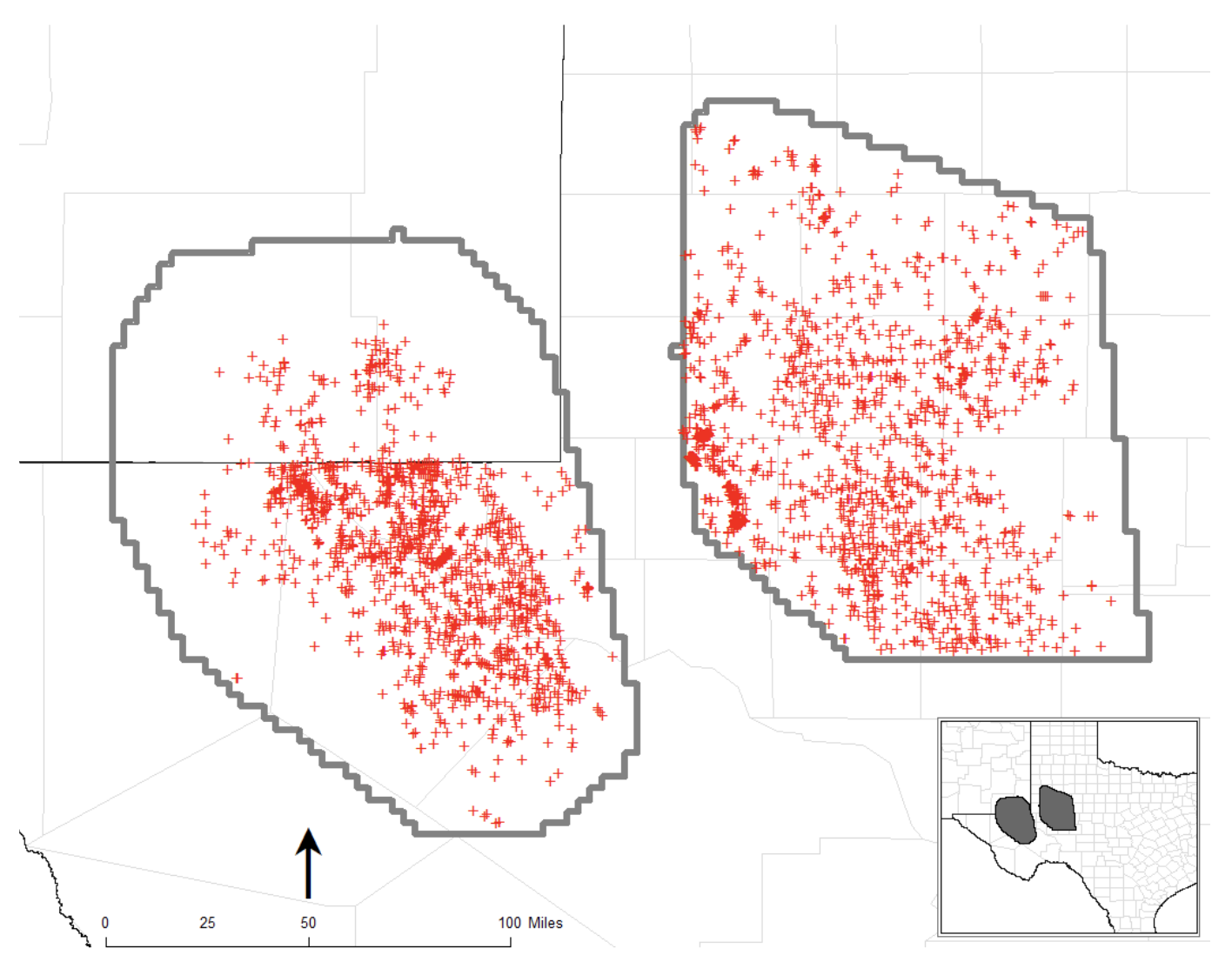
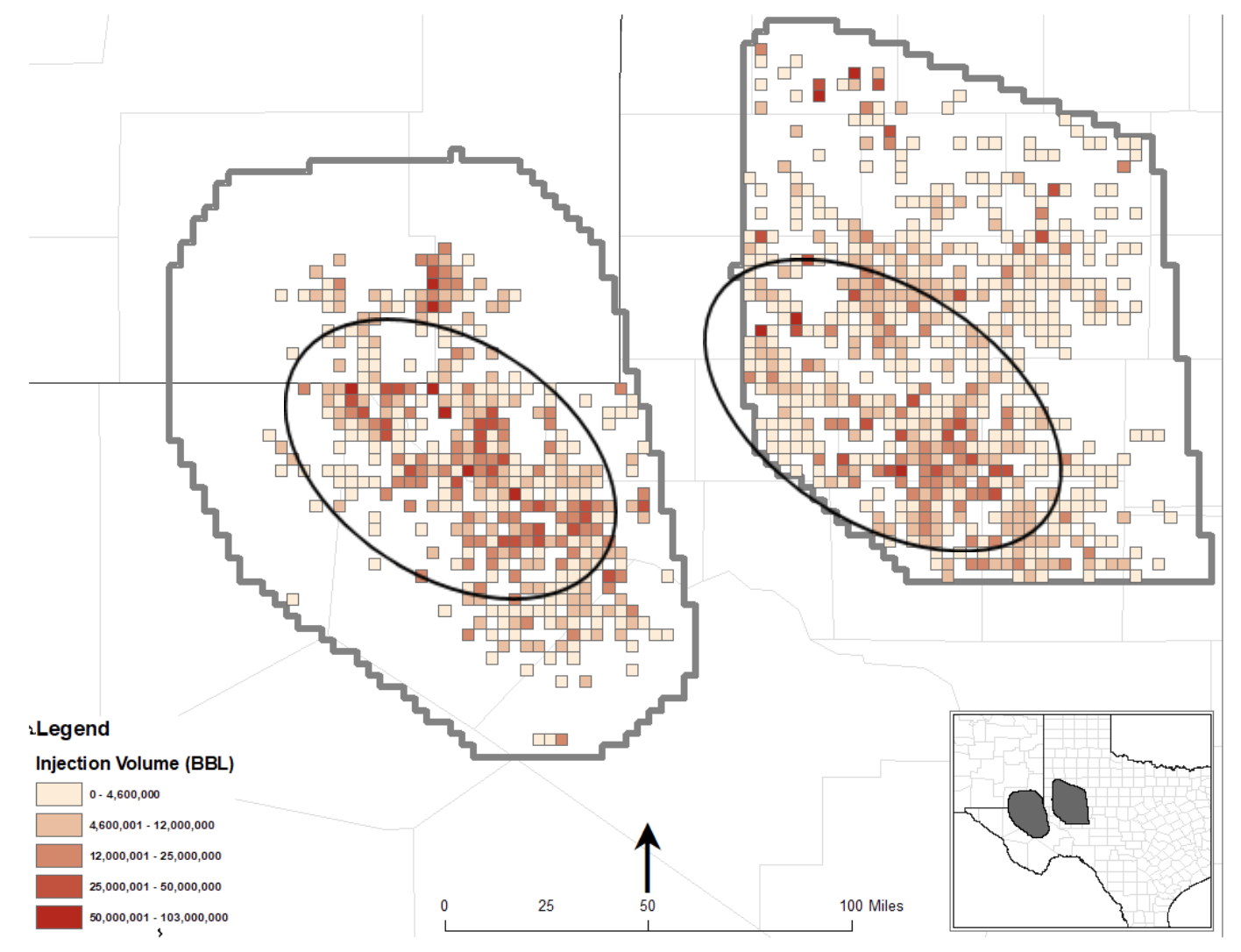
The location of disposal wells with a completed interval intersecting the DMG and SA is depicted in Figure 3. As the top and bottom of a completed well interval can extend beyond a single geologic horizon, injection volumes were apportioned based on the fraction of the interval within the DMG and SA units.
Figure 2. Depth to top of formation for the DMG and SA. Contours in feet from mean sea level. Source: Enverus.
The location of disposal wells with a completed interval intersecting the DMG and SA is depicted in Figure 3. As the top and bottom of a completed well interval can extend beyond a single geologic horizon, injection volumes were apportioned based on the fraction of the interval within the DMG and SA units.
Simulation
Numerical fluid flow simulations were performed using the United States Geological Survey (USGS) groundwater flow modeling software MODFLOW. The TWDB grid was used to discretize the hydrogeologic systems (the DMG and SA were treated independently). Steady-state simulations were run to determine reservoir pressure conditions prior to significant water disposal (i.e., pre-1983 period). Transient simulations were then run to determine reservoir pressure evolution from 1983 to 2017. Model sensitivities were evaluated using various initial pressure conditions, boundary conditions, and rock property values/distributions.
Results
Within both DMG and SA models, the primary influences on reservoir pressure were instantaneous injection rate, cumulative injection volume, proximal injection, and local geologic/hydrogeologic conditions, with cumulative injection volume having the dominant effect on simulation results.
While near-wellbore changes in reservoir pressure tended to be transitory (i.e., pressure dissipates relatively quickly when injection ceases), model results suggest background reservoir pressure increases associated with cumulative water injected to be much longer lasting. To investigate pressure persistence, the SA model was re-run from 1983 to 2033 with the same conditions for 1983 to 2017, but then no injection from 2018 to 2033. Model results suggest that 15 years after injection, elevated background reservoir pressures largely remain, especially in relatively high-pressure areas.
Discussion and Model Limitations
While the work presented provides a useful first approximation of Permian Basin shallow disposal effects on reservoir pressure, it also exposes limitations of what can be done with current publicly available information. Due to limited data availability and often dubious data quality, these necessarily coarsely discretized models represent highly idealized versions of extremely complicated dynamic natural systems. The simulations, developed to assess relative influences on reservoir pressure at regional-scale, are not designed to provide local-scale estimates of absolute pressure. For more rigorous and finer-scale application, substantially better characterization of rock- and fluid- properties and more qualified high-resolution volume and pressure data must be accessed/used (which, at this time, is only available privately). In the absence of such data, while more detailed or refined models could be developed, validity beyond the current resolution considered would be difficult to verify.
Summary
The presented subsurface fluid flow models are intended as an initial tool to understand regional reservoir pressure changes in the Permian Basin due to past subsurface produced water disposal. And while it is generally accepted that both disposal volumes and number of well locations will continue to rise over the coming years, it is uncertain when and where the increases will occur, and by how much, making any specific forecasting difficult. Nevertheless, current results suggest:
- Reservoir pressure changes are area-specific,
- Cumulative injection volume exerts the strongest control on long-term background pressure change,
- Increased reservoir pressures do not readily dissipate, potentially persisting over decadal time scales.
These broad conclusions are important to take into consideration as the industry continues to address water management options for the Permian Basin.
Our Capabilities
If you are investigating Permian Basin water management challenges and opportunities, B3 Insight can help. Our experts have worked with stakeholders across the value chain to help make better decisions through data, reports, bespoke research, and consulting services.
About B3 Insight
B3 delivers technology and insight that enable customers to make responsible and profitable decisions about water resources. B3’s flagship product is the leading SaaS oilfield water intelligence platform for the oil and gas industry. B3 provides in-depth water data for producing basins in Texas and New Mexico in a user-friendly, transparent manner that delivers actionable intelligence across water midstream, exploration and production (E&P), oilfield services and finance companies. B3 provides data and analytics to help customers evaluate assets, enhance operational efficiencies, mitigate risk, allocate capital, and benchmark performance. For more information, visit B3insight.com.